Table of Contents
Collaborative robot are designed to work alongside humans, sharing the same workspace and often performing tasks that were previously done manually. Commonly referred to as cobots, they usually take the form of a robot arm equipped with interchangeable grippers for various tasks. Unlike large industrial robots, collaborative robot are compact, lightweight, and engineered with safety in mind, enabling them to operate in close proximity to people. This design focus naturally imposes constraints on the size and specifications of internal components, particularly actuators, which in turn limits payload capacity compared to their larger industrial counterparts.
An actuator is a drive module that combines a motor and a reducer to move the robot’s joints. Various types of reducers are used, such as planetary gears, harmonic drives, RV gears, and cycloidal reducers, each chosen to match the operational demands of different industrial environments. As cobots evolve toward more compact and lightweight designs, actuator and reducer engineering has shifted toward minimizing both thickness and weight without compromising performance.
Our Bonsystems Cycloid Smart Actuator (BCSA) series was developed in direct response to this trend. Thickness, in particular, is more than a matter of saving space. It has direct implications for robot design, movement, and operational efficiency. Below, we examine the two major ways actuator thickness impacts collaborative robot performance.
1. Expanded Design Flexibility and Implementation Freedom
Inside a collaborative robot, components such as motors, reducers, bearings, controllers, sensors, and cables are tightly packed. To ensure smooth motion and avoid interference between parts, internal layout and wiring design must be carefully optimized. A thinner actuator reduces joint volume, making internal space usage far more efficient.
With more available space, designers can go beyond simple size reduction and achieve a larger rotation radius. This allows the robot arm to move more naturally and operate without restrictions even in tight workspaces. For example, traditional gear motor structures often forced bulky lateral designs, but thinner actuators enable slim, human-arm-like profiles. This not only benefits mechanical performance but also allows for more elegant and ergonomic aesthetics, such as curved surfaces and seamless silhouettes.
If thin actuators can still maintain high torque output, they can be used not only in lightweight cobots but also in industrial applications requiring higher payload capacity. Bonsystems achieves this by applying a proprietary cycloidal tooth profile, distributing load efficiently and ensuring stable output even in thin, compact builds.
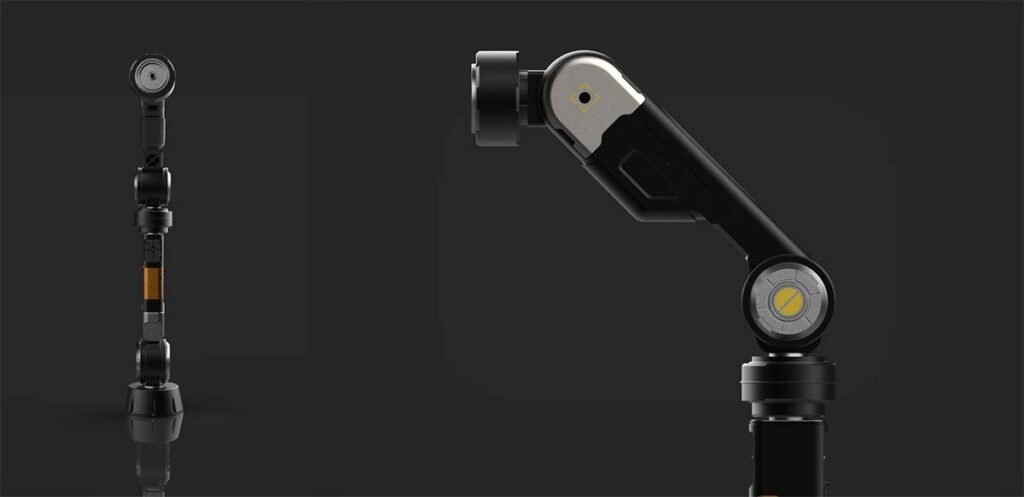

2. Weight Reduction and Performance Stability
Reducing robot weight is not simply about lowering mass. It directly affects center of gravity, stability, and overall drive performance. Heavier components increase joint load, which can lead to reduced control stability, higher energy consumption, and more heat generation. For cobots, which perform repetitive motions near humans, stability is essential, making weight reduction a key design goal.
A thinner, lighter actuator lowers the robot’s center of gravity, reducing sway and improving responsiveness during operation. This boosts energy efficiency and, in battery-powered mobile cobots, can extend operational time.
However, weight reduction cannot come at the expense of structural strength. Low-strength materials such as basic plastics are unsuitable for high-torque applications. Instead, lightweight yet strong solutions such as high-grade aluminum housings with robust structural design are required. Our BCSA actuators are built to meet both criteria, ensuring durability alongside reduced mass.
BCSA Series Highlights
The BCSA is a cycloidal-based smart actuator that integrates core control features such as drivers and encoders as needed, depending on the robot’s design requirements. Optimized for collaborative robot arms and humanoid structures, it delivers high torque output in a slim form factor.
The BCSA series offers reduction ratios from 11:1 to 49:1, enabling optimal joint-specific configuration. This means a humanoid robot can be fully equipped using only BCSA units, ensuring consistent performance across all joints. This is one of Bonsystems’ key competitive strengths.
For maintenance efficiency, the reducer and motor are installed separately. This allows either component to be replaced individually without disassembling the entire unit, reducing downtime and service costs. The aluminum anodized finish provides corrosion resistance, weight savings, and a premium appearance.
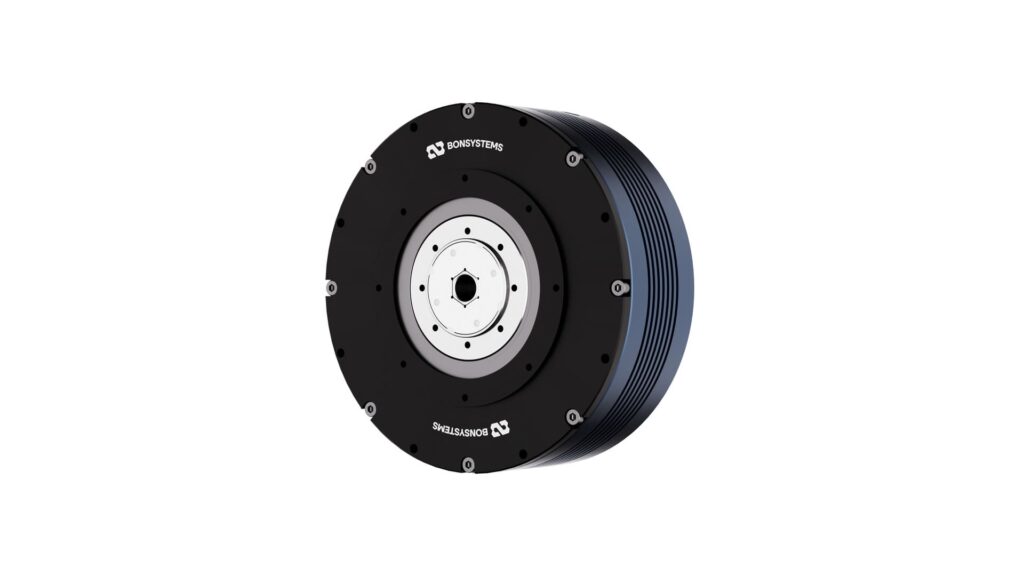

Frameless Motor in a Hollow Shaft Actuator
Another engineering approach to maximize collaborative robot efficiency is the hollow shaft design. By keeping the actuator’s central shaft open, cables, fluid lines, or sensor wires can pass internally, eliminating the need for external routing and enabling cleaner, safer joint layouts.
We combine this with frameless motors, which have no separate housing and can be integrated directly into the drive assembly. This removes unnecessary external casing and greatly improves internal space utilization. As a result, both diameter and thickness can be minimized without sacrificing torque, making it ideal for slim, compact cobot designs.
This approach not only optimizes space but also reduces cable exposure, lowering the risk of wear or damage. It also improves the robot’s external appearance by eliminating bulky external wiring, creating a smoother, more refined profile. Ultimately, a hollow shaft actuator with a frameless motor meets all the key requirements for cobots: space efficiency, stable wiring, and unrestricted joint motion, enabling high performance even in limited spaces.
The BCSA series represents years of research and testing, consolidating the technical features required for collaborative robot applications. The latest version is scheduled for release in August, with full specifications available on the Bonsystems product introduction page.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q. Why is actuator thickness important in collaborative robot design?
Actuator thickness directly affects the volume of the robot’s joint section and the efficiency of internal space utilization. When the thickness is reduced, interference between components is minimized and the rotation radius can be increased. This allows smooth operation even in confined workspaces.
Q. What is the most notable feature of the BCSA V4 series?
The BCSA V4 series uses a cycloidal-based design to deliver stable high torque output even with a slim profile. It supports a wide range of reduction ratios from 11:1 to 49:1, enabling optimization for each robot joint. The reducer and motor are installed separately, which simplifies maintenance.
Q. What are the advantages of a hollow shaft structure with a frameless motor?
A frameless motor has no housing and can be directly integrated into the drive unit, reducing both diameter and thickness. When combined with a hollow shaft structure, cables, sensor lines, and fluid pipes can be routed internally, minimizing wiring interference and keeping the exterior slim.
Q. What benefits come from reducing external cables?
Fewer exposed cables significantly lower the risk of wear, bending, and environmental damage. Maintenance time is reduced, and the robot arm retains a smooth exterior, enhancing both design quality and system reliability.
Q. In what environments is the BCSA V4 series especially suitable?
The BCSA V4 series is optimized for collaborative robot and humanoid designs where space is limited and high torque is required. Its slim profile, lightweight build, and stable wiring structure allow it to perform effectively in environments that demand complex multi-joint motion.
